Spaced repetition and retrieval practice are two powerful learning techniques that are often used in microlearning to enhance memory retention and long-term learning. Here's a summary of these concepts:
Spaced Repetition:
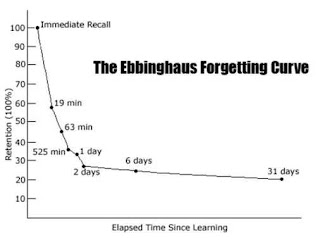
Spaced repetition is a learning technique that involves reviewing material at increasing intervals over time. The idea is to strategically space out review sessions so that you revisit the material at the point when you're about to forget it. This technique is based on the spacing effect, which suggests that information is better retained when it is reviewed multiple times over spaced intervals rather than all at once. Spaced repetition algorithms determine the timing of review sessions based on the difficulty of the material and the learner's performance.
Retrieval Practice:
Retrieval practice is a learning strategy that involves actively recalling information from memory. Instead of simply rereading or reviewing material, retrieval practice requires learners to actively retrieve information without the aid of external cues. This process strengthens memory retrieval pathways and improves long-term retention. Retrieval practice can take various forms, including self-quizzing, flashcards, and practice tests. The act of recalling information from memory reinforces neural connections associated with that information, making it easier to retrieve in the future.
Microlearning:
Microlearning is an approach to learning that involves delivering content in small, focused units. Instead of lengthy lectures or courses, microlearning breaks down information into bite-sized chunks that are easier to digest and retain. Microlearning modules are typically brief, ranging from a few minutes to around 15 minutes in length. This format is well-suited to spaced repetition and retrieval practice because it allows for frequent, targeted review sessions that reinforce learning without overwhelming the learner.
Integration of Spaced Repetition and Retrieval Practice in Microlearning:
Spaced repetition and retrieval practice are highly compatible with the principles of microlearning. By incorporating these techniques into microlearning modules, educators can maximize learning outcomes in a minimal amount of time. Learners engage with material through repeated retrieval practice, reinforcing their understanding and retention of key concepts. Spaced repetition algorithms can be used to schedule review sessions within microlearning modules, ensuring that learners revisit material at optimal intervals to promote long-term retention.
Benefits of Spaced Repetition and Retrieval Practice in Microlearning:
Improved retention: Spaced repetition and retrieval practice promote long-term retention of information by reinforcing memory retrieval pathways.
Efficient learning: Microlearning delivers content in small, manageable units, making it easier for learners to engage with material and incorporate spaced repetition and retrieval practice into their study routine.
Personalized learning: Spaced repetition algorithms can adapt to individual learning needs, optimizing the timing of review sessions based on each learner's performance.
Enhanced engagement: Retrieval practice actively engages learners in the learning process, promoting deeper understanding and active recall.
In conclusion, spaced repetition and retrieval practice are effective learning techniques that can be seamlessly integrated into microlearning to enhance memory retention and learning outcomes. By incorporating these strategies into microlearning modules, educators can create engaging and effective learning experiences that promote long-term retention of key concepts.
Comments
Post a Comment